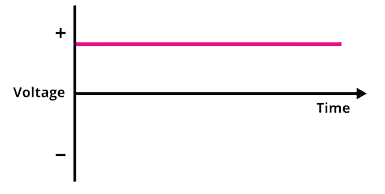 |  |
| Type: Pure and pulsating. | Type: Sinusoidal, Trapezoidal, Triangular, Square |
| In DC, the flow of electric charge is uni-directional, maintaining a constant polarity. | In AC, the direction of the current reverses periodically. |
| Direct current can be stored in batteries. | Alternating current cannot be stored. |
| DC voltage remains constant over time, which makes it suitable for powering electronic devices. | The voltage and current in AC systems oscillate sinusoidally. |
| The frequency of direct current is zero. | The frequency of alternating current is 50Hz or 60Hz depending on the country. |
| DC is commonly used in electronics, batteries, and low-voltage applications. | AC is commonly used in household electrical systems, industrial machinery, and power distribution grids. |